1 Ton Equal To How Many Btu
Treneri
May 13, 2025 · 6 min read
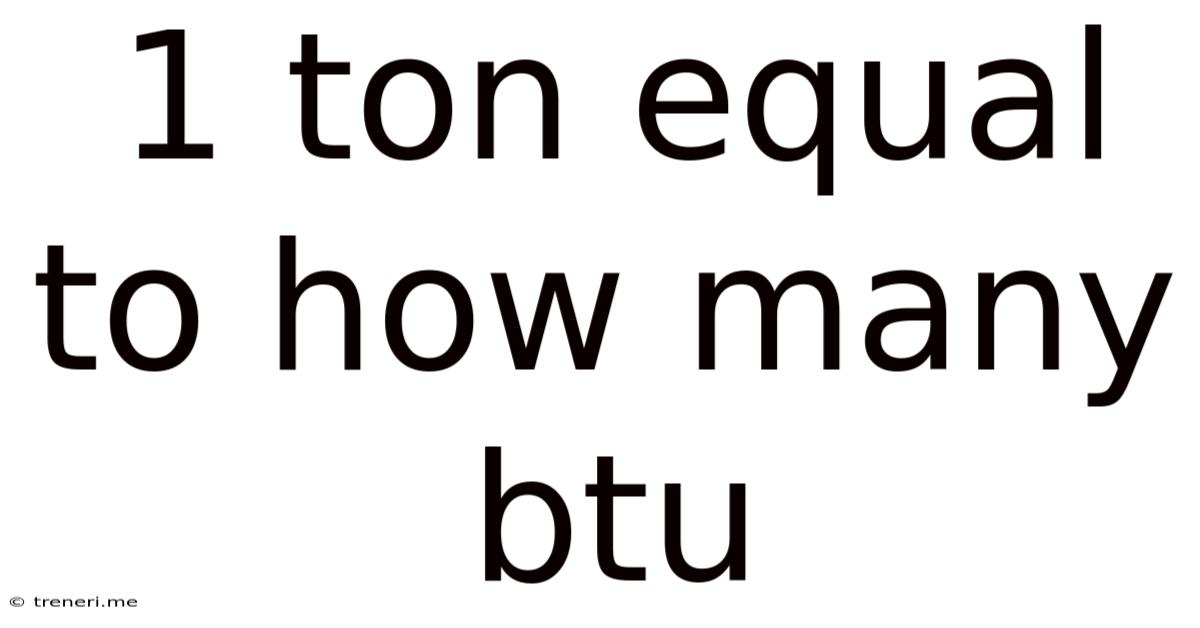
Table of Contents
1 Ton Equal to How Many BTU? Understanding Air Conditioning Capacity
Understanding the capacity of your air conditioning unit is crucial for ensuring your home stays comfortably cool during the hottest months. Often, you'll see air conditioner capacities expressed in "tons," a somewhat archaic unit of measurement that can be confusing for many homeowners. So, the burning question is: 1 ton equal to how many BTU? The answer, and the underlying concepts, are explored in detail below.
Understanding BTUs and Tons in Air Conditioning
Before diving into the conversion, let's define the key terms:
What is a BTU?
BTU stands for British Thermal Unit. It's a unit of energy representing the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In the context of air conditioning, a BTU measures the cooling power of a unit. A higher BTU rating means the unit can remove more heat from a space.
What is a Ton in Air Conditioning?
A "ton" in air conditioning refers to the cooling capacity of the unit, historically relating to the amount of heat a ton of ice could melt in 24 hours. This historical reference point is why the "ton" is still used, despite seeming somewhat out of place in modern measurements.
The Conversion: 1 Ton = How Many BTU?
The standard conversion is: 1 ton of air conditioning equals 12,000 BTUs. This is a fundamental relationship you need to keep in mind when sizing your air conditioner.
This means a 2-ton unit is equivalent to 24,000 BTUs, a 3-ton unit is 36,000 BTUs, and so on. This direct proportionality simplifies the calculation for units of different capacities.
Why is this conversion important?
Accurately determining the BTU requirement for your space is essential for efficient and effective cooling. A unit that's too small will struggle to cool your home adequately, leading to higher energy bills and discomfort. Conversely, an oversized unit will cycle on and off frequently, preventing proper dehumidification and potentially leading to higher energy consumption and uneven cooling.
Factors Affecting BTU Requirements
Calculating the precise BTU requirements for your home isn't simply a matter of plugging numbers into a formula. Several factors influence the necessary cooling capacity:
1. Square Footage: The Size of Your Space
The larger the area you need to cool, the higher the BTU requirement. However, square footage alone isn't the only determinant.
2. Climate and Geographic Location: The External Heat Load
The climate you live in drastically affects the cooling load. Homes in hotter, more humid regions require air conditioners with significantly higher BTU ratings than those in milder climates. Consider average summer temperatures and humidity levels in your area.
3. Insulation and Window Efficiency: Reducing Heat Gain
The insulation quality of your home plays a vital role. Well-insulated homes with energy-efficient windows retain cool air more effectively, requiring fewer BTUs to maintain a comfortable temperature. Poorly insulated homes will need a higher BTU capacity to compensate for heat loss.
4. Number of Windows and Their Orientation: Sunlight Exposure
The number of windows and their orientation relative to the sun significantly impact the heat gain within your home. South-facing windows, for instance, receive more direct sunlight and therefore contribute to a higher cooling load.
5. Ceiling Height: Volume of Air to Cool
Higher ceilings mean a greater volume of air to cool, increasing the required BTU rating. This factor often gets overlooked in basic calculations but is crucial for accuracy.
6. Number of Occupants and Appliances: Internal Heat Generation
People, appliances, and lighting generate heat. The more occupants and heat-producing appliances in your home, the higher the BTU requirement. Consider factors like the number of people living in the house, the use of computers, and other electronics.
7. Desired Temperature Differential: How Cool You Want It
The desired temperature difference between the outside and inside air influences the BTU needs. A larger temperature differential requires a higher BTU output to achieve and maintain the desired internal temperature.
Calculating BTU Requirements: An Overview
While a precise calculation requires professional assessment, several online calculators provide estimates based on the factors mentioned above. These calculators often ask for details such as:
- Square footage: The total area of the space to be cooled.
- Ceiling height: The height of the ceilings in the space.
- Number of windows: The total number of windows in the space.
- Climate zone: Your geographical location and its climate classification.
- Insulation level: The quality of the insulation in your home (poor, average, good).
These calculations provide a reasonable starting point, but remember that they are estimates.
Professional Assessment: Ensuring Accurate Sizing
For the most accurate BTU requirement, it's highly recommended to consult a qualified HVAC professional. They'll conduct a thorough assessment of your home, taking into account all relevant factors, to determine the optimal air conditioner size for your specific needs. This ensures efficient and comfortable cooling while maximizing energy savings.
This professional assessment eliminates the guesswork and helps avoid costly mistakes in selecting an underpowered or overpowered unit. They'll consider not only the BTU rating but also other critical aspects of system design, such as ductwork and refrigerant type.
Beyond BTU: Other Important Considerations
While the BTU rating is a critical factor, it's not the only aspect to consider when choosing an air conditioner. Other important considerations include:
- SEER rating: Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER) measures the unit's energy efficiency over an entire cooling season. A higher SEER rating indicates greater energy efficiency.
- EER rating: Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) measures the unit's energy efficiency under specific conditions. This is often used as a comparison metric between different models.
- Noise levels: Consider the noise level produced by the unit, especially if it will be located near living areas.
- Features: Some units offer additional features such as programmable thermostats, humidity control, and air filtration.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Air Conditioner
Understanding the relationship between tons and BTUs is essential for selecting the right air conditioning unit for your home. While the conversion of 1 ton = 12,000 BTUs provides a fundamental understanding, accurately determining the cooling needs of your home requires consideration of multiple factors, including square footage, climate, insulation, and internal heat loads. Always prioritize consulting a qualified HVAC professional for a comprehensive assessment to ensure your home stays comfortably cool and you enjoy efficient energy consumption. Don't just focus on the BTU; consider the overall system efficiency and features to make an informed decision that benefits both your comfort and your wallet. A properly sized and energy-efficient air conditioning system contributes significantly to a comfortable and cost-effective home environment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Quotient Of 14 And 7
May 13, 2025
-
90 Days From November 6 2024
May 13, 2025
-
3 Gallons Equal How Many Quarts
May 13, 2025
-
How Many Days Is 345 Hours
May 13, 2025
-
4 5 Divided By 1 8
May 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 Ton Equal To How Many Btu . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.