1 Ton Is Equal To How Many Btu
Treneri
May 12, 2025 · 5 min read
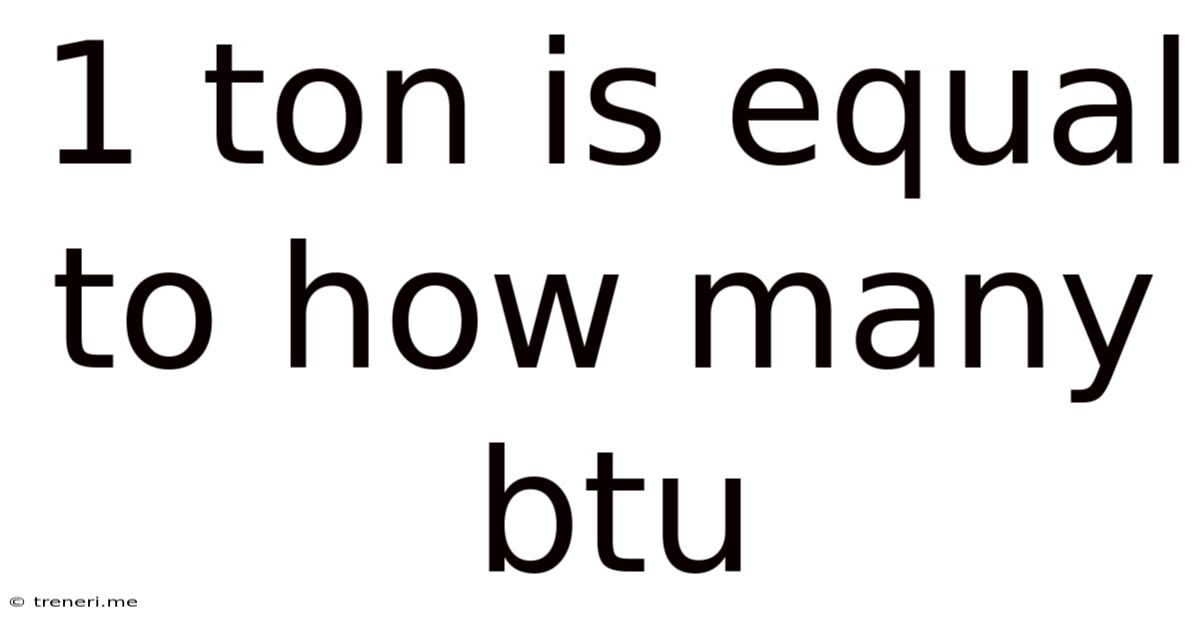
Table of Contents
1 Ton is Equal to How Many BTU? Understanding HVAC Capacity
The question, "1 ton is equal to how many BTU?" is a common one, particularly for those navigating the world of heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC). Understanding the relationship between tons and BTUs is crucial for selecting the right sized air conditioner or heat pump for your home or business. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into this crucial relationship, exploring the underlying principles and helping you make informed decisions about your HVAC needs.
Understanding BTU (British Thermal Unit)
Before we dive into the ton-BTU conversion, let's establish a clear understanding of the BTU. A BTU (British Thermal Unit) is a unit of energy. Specifically, it's the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. In the HVAC context, BTUs represent the cooling or heating capacity of a system. A higher BTU rating indicates a greater capacity to cool or heat a space.
Understanding Tons of Refrigeration
The term "ton" in HVAC refers to the refrigeration ton, which is a unit of power, not weight. It's derived from the cooling capacity of melting one ton of ice in 24 hours. This seemingly archaic unit remains a standard in the HVAC industry. It’s a way to easily gauge the cooling power of a system, simplifying comparison for consumers.
The Conversion: 1 Ton = 12,000 BTU/hour
The fundamental conversion is this: 1 ton of refrigeration is equal to 12,000 BTUs per hour (BTU/hr). This means a 1-ton air conditioner can remove 12,000 BTUs of heat from a space every hour. Similarly, a 1-ton heat pump can add 12,000 BTUs of heat to a space every hour.
Why 12,000 BTU/hr?
The 12,000 BTU/hr figure originates from the historical definition of a refrigeration ton. The amount of heat required to melt one ton (2000 pounds) of ice in 24 hours is approximately 288,000 BTUs. Dividing this by 24 hours gives us the hourly rate of 12,000 BTU/hr.
Calculating Your HVAC Needs: Beyond the Ton
While the 12,000 BTU/hr per ton conversion is a useful starting point, it’s crucial to remember that selecting the right HVAC system involves more than just this simple conversion. Several factors influence the appropriate BTU rating for your specific needs. These factors include:
1. Square Footage of the Space
The size of the area you need to heat or cool is a primary determinant. Larger spaces naturally require more powerful systems with higher BTU ratings. However, square footage alone isn't sufficient for accurate sizing.
2. Climate and Insulation
Your local climate significantly impacts the cooling and heating load. Hotter climates naturally demand higher BTU systems. The quality of your home's insulation also plays a significant role. Better insulation reduces heat loss in winter and heat gain in summer, potentially allowing you to choose a smaller, more energy-efficient system.
3. Number of Windows and their Orientation
Windows are significant contributors to heat gain in summer and heat loss in winter. The number of windows and their orientation (south-facing windows gain more heat) affect your energy needs.
4. Number of Occupants and Appliances
The presence of people, appliances, and electronic devices generates heat. More people and appliances will increase the heating load, requiring a larger system.
5. Ceiling Height
Higher ceilings create larger spaces to heat or cool, which generally translate to higher BTU requirements.
6. Desired Temperature Difference
The difference between the indoor temperature you desire and the outdoor temperature dictates the cooling or heating load. A larger temperature difference requires a more powerful system.
Using BTU Calculators and Professional Advice
Determining the precise BTU requirement for your specific situation can be complex. Using online BTU calculators can provide an estimate based on inputting your home's specifications. However, these calculators provide estimates, not precise figures.
For optimal results, consult a qualified HVAC professional. Professionals conduct comprehensive load calculations that account for all relevant factors. This ensures that the chosen system provides sufficient cooling or heating capacity while avoiding oversized or undersized equipment. Oversized systems can lead to shorter cycling times, reduced humidity control and increased energy costs. Undersized systems struggle to maintain comfortable temperatures and constantly run at full capacity.
Beyond BTU and Tons: SEER and EER Ratings
Beyond BTU and tons, understanding SEER (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and EER (Energy Efficiency Ratio) is critical for making informed decisions. These ratings indicate the energy efficiency of an HVAC system. A higher SEER or EER rating translates to lower energy consumption and lower operating costs.
SEER is a seasonal measure, reflecting the system's efficiency across an entire cooling season. EER measures efficiency under specific conditions. Both are important metrics to consider when choosing a system that balances cooling power with energy efficiency.
Troubleshooting Common Issues with HVAC Systems
Understanding BTU requirements is essential for avoiding common HVAC problems. Here are some of them:
1. Insufficient Cooling or Heating
This issue often points to an undersized system that cannot meet the cooling or heating load.
2. Excessive Cycling
Oversized systems cycle on and off frequently, leading to poor humidity control, temperature fluctuations, and higher energy bills.
3. High Energy Bills
Both oversized and undersized systems can result in high energy bills. An oversized unit will cycle too often while an undersized unit struggles to meet the demands, running continuously.
4. Poor Indoor Air Quality
An improperly sized or poorly maintained system can compromise indoor air quality.
Conclusion: Accurate Sizing is Key
Choosing the right HVAC system is crucial for comfort, energy efficiency, and longevity. While the conversion of 1 ton to 12,000 BTU/hr is a foundational piece of this knowledge, it is just one part of the equation. A holistic approach that accounts for climate, home characteristics, and professional load calculations ensures that your chosen system effectively meets your needs for years to come. Don't rely solely on simple conversions; consult professionals for accurate assessment and optimal system selection. This investment will deliver long-term savings and enhanced comfort.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Cuantos Dias Faltan Para El 2 De Junio
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Seconds In 20 Years
May 12, 2025
-
90 Days From October 25 2023
May 12, 2025
-
What Uv Do You Tan At
May 12, 2025
-
6 1 4 3 5 8
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about 1 Ton Is Equal To How Many Btu . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.