China's Economy: Real Estate's Enduring Importance
Treneri
Jun 01, 2025 · 7 min read
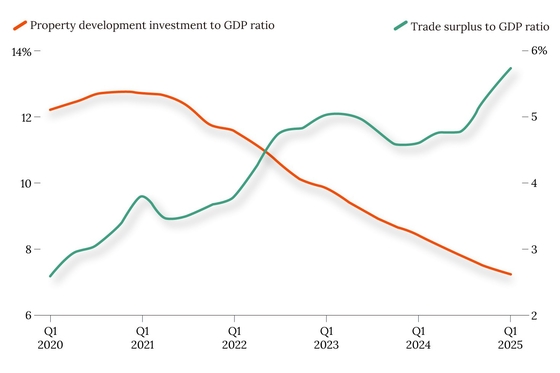
Table of Contents
China's Economy: Real Estate's Enduring Importance
China's economic miracle, a period of unprecedented growth spanning decades, has been inextricably linked to its real estate sector. For many years, this sector served as an engine of growth, driving investment, employment, and overall economic expansion. However, the past few years have witnessed a significant slowdown and even a crisis in the real estate market, raising serious concerns about its future and its impact on the broader Chinese economy. Understanding the enduring importance of real estate in China, even amidst the current challenges, is crucial for comprehending the country's economic trajectory and predicting future trends. This article will delve into the complex relationship between China's economy and its real estate sector, exploring its historical significance, the current crisis, and its potential future impact. For investors, policymakers, and anyone interested in the global economy, grasping this dynamic is paramount.
The Rise of Real Estate as an Economic Engine
The rapid expansion of China's real estate sector began in the late 1990s and accelerated throughout the 2000s. Several factors contributed to this boom:
-
Urbanization: China experienced a massive wave of urbanization, with millions of rural residents migrating to cities in search of better opportunities. This surge in urban population fueled an immense demand for housing.
-
Government Policies: Government policies actively supported the real estate sector. Tax incentives, subsidized loans, and infrastructure development projects created a favorable environment for investment and growth. These policies often prioritized rapid growth over long-term sustainability.
-
Foreign Investment: Foreign investment poured into the Chinese real estate market, further driving development and construction.
-
Speculation: Significant speculation fueled the market, leading to inflated prices and a self-reinforcing cycle of investment.
The consequences of this rapid growth were substantial. Real estate became a major contributor to GDP growth, accounting for a significant portion of investment and employment. Construction became a massive industry, employing millions of workers directly and indirectly. Related industries like cement, steel, and furniture also experienced significant booms. The sector fueled local government finances through land sales, which often served as a primary revenue source. However, this reliance created vulnerabilities.
The Current Crisis and its Implications
The past few years have witnessed a significant slowdown and even a crisis in China's real estate sector. Several factors contributed to this downturn:
-
Over-Leveraging: Developers accumulated massive amounts of debt, financing ambitious projects with borrowed money. As interest rates rose and credit tightened, many developers found themselves struggling to repay their loans.
-
Falling Demand: A combination of factors, including slower economic growth, stricter regulations on mortgages, and concerns about property bubbles, led to a decline in demand for new housing.
-
Government Regulations: The government introduced stricter regulations to curb speculation and control the rapid growth of the sector. These included measures to limit borrowing by developers, increase capital requirements, and prevent excessive price increases.
-
The "Three Red Lines" Policy: Introduced in 2020, this policy limited developers' debt-to-asset ratios, net debt-to-equity ratios, and short-term debt-to-long-term debt ratios. This aimed to reduce systemic risks but also constrained developers' ability to fund new projects.
-
Evergrande's Collapse: The near-collapse of Evergrande, one of China's largest real estate developers, in 2021 served as a stark reminder of the fragility of the sector and the potential systemic risks. Its troubles triggered a chain reaction, impacting other developers and unsettling investor confidence.
The implications of this crisis are far-reaching:
-
Economic Slowdown: The decline in the real estate sector has contributed to a broader economic slowdown in China, impacting growth rates and employment.
-
Financial Instability: The debt crisis in the real estate sector poses risks to the financial system, with concerns about the potential for defaults and contagion effects.
-
Social Unrest: Delays in project completion and concerns about property values have led to social unrest, with buyers and investors expressing their grievances.
-
Local Government Finances: The decline in land sales has severely impacted the finances of local governments, which relied heavily on this revenue stream. This has led to budget shortfalls and potential difficulties in funding public services.
The Enduring Importance and Path Forward
Despite the current crisis, the real estate sector remains of enduring importance to the Chinese economy. Housing remains a fundamental need, and urbanization continues, albeit at a slower pace. The sector still employs millions and plays a significant role in infrastructure development. However, a fundamental shift is necessary. The previous model of rapid, debt-fueled growth is unsustainable. The path forward requires a focus on:
-
Sustainable Development: Prioritizing quality over quantity, building affordable housing, and reducing reliance on debt financing.
-
Regulatory Reform: Implementing more effective regulations to curb speculation, manage risk, and ensure transparency.
-
Financial Restructuring: Assisting financially stressed developers to restructure their debt and prevent defaults.
-
Diversification of Local Government Revenue: Reducing reliance on land sales and exploring alternative revenue streams to fund public services.
-
Improved Consumer Protection: Implementing measures to protect homebuyers and ensure the timely completion of projects.
Scientific and Economic Analogies
The Chinese real estate crisis can be compared to other historical financial crises, such as the US subprime mortgage crisis of 2008. Both involved excessive leveraging, rapid growth fueled by speculation, and ultimately led to a significant economic downturn. However, the Chinese context is unique, with its state-led economic model and the significant role of local governments. This makes addressing the crisis more complex.
Another relevant analogy is that of a biological organism. The real estate sector was like a rapidly growing organ, consuming significant resources. Its uncontrolled growth created imbalances and vulnerabilities. The current crisis represents a period of readjustment, where the organism needs to shed excess weight and restructure to achieve sustainable health.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: Will China's real estate market collapse completely?
A1: A complete collapse is unlikely, given the fundamental need for housing and the government's commitment to stabilizing the sector. However, a period of significant restructuring and consolidation is anticipated, leading to a smaller, more sustainable market.
Q2: What is the government doing to address the crisis?
A2: The Chinese government has implemented a range of measures, including easing monetary policy, providing financial support to developers, and strengthening regulations to curb speculation. The effectiveness of these measures remains to be seen.
Q3: How will the real estate crisis impact foreign investors?
A3: The crisis has already impacted foreign investors, with some experiencing losses and reduced returns. Future investments will require a more cautious approach, with a thorough understanding of the risks involved.
Q4: What are the long-term prospects for China's real estate sector?
A4: The long-term prospects depend on the success of government policies in stabilizing the sector, addressing debt issues, and promoting sustainable development. A smaller, healthier sector focused on affordable housing and sustainable practices is the most likely scenario.
Q5: How does this crisis affect global markets?
A5: The ripple effects are felt globally, particularly in commodity markets (steel, cement), impacting global supply chains and potentially influencing inflation worldwide. Investor confidence in emerging markets is also affected, causing some capital flight.
Conclusion and Call to Action
China's real estate sector, once a powerful engine of economic growth, is currently undergoing a period of significant transformation. The crisis highlights the risks associated with rapid, debt-fueled expansion and the importance of sustainable development. While a complete collapse is unlikely, the sector will undoubtedly be smaller and less influential than it was in its heyday. The long-term impact on the Chinese economy remains to be seen, but its enduring importance, albeit in a reformed capacity, is undeniable. To stay informed on this crucial aspect of the global economy, continue exploring related articles and analyses. Understanding the evolving dynamics of China’s real estate sector is essential for navigating the complex landscape of global finance and investment.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Madame Clairevoyants June 2 2025 Horoscope
Jun 02, 2025
-
Love Island Usa Season 7 Where To Watch
Jun 02, 2025
-
Ezb Zinsen Letzter Zinssenkung Am Donnerstag
Jun 02, 2025
-
Chelsea Signs Dario Essugo From Sporting Cp
Jun 02, 2025
-
Drapers French Open Exit Bubliks Masterclass
Jun 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about China's Economy: Real Estate's Enduring Importance . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.