How Many Milliseconds Are In 1 Second
Treneri
Apr 05, 2025 · 6 min read
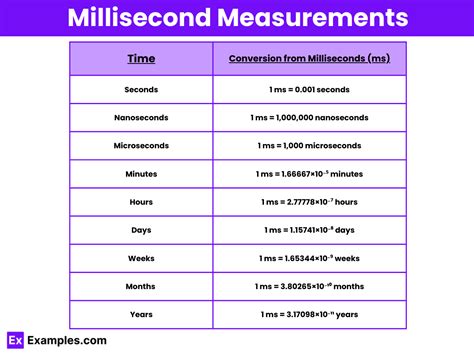
Table of Contents
How Many Milliseconds Are in 1 Second? A Deep Dive into Time Measurement
The seemingly simple question, "How many milliseconds are in 1 second?" opens a fascinating window into the world of time measurement, its history, and its crucial role in modern technology. The answer, of course, is 1000, but understanding why this is so, and the implications of this fundamental unit, is far more complex and rewarding. This article will explore the intricacies of milliseconds, their relationship to seconds and other units of time, and their significance across various fields.
Understanding the Metric System and Time Measurement
Before delving into milliseconds, let's establish a solid foundation in the metric system, the foundation upon which this unit is built. The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is a decimal system based on powers of ten. This means that units are related by factors of 10, making conversions remarkably straightforward.
This system is universally used in scientific and technological contexts because of its inherent simplicity and consistency. It's crucial to grasp this fundamental principle to fully understand milliseconds and their place within the broader framework of time measurement. The base unit of time in the SI system is the second.
From Seconds to Milliseconds: A Decimal Descent
The prefixes used in the metric system allow us to easily create units representing multiples or fractions of the base unit. For milliseconds, the prefix is "milli," meaning one-thousandth. Therefore:
- 1 millisecond (ms) = 1/1000 of a second
- 1 second = 1000 milliseconds
This simple conversion is essential in numerous applications. It's the cornerstone for understanding how computers process information, how high-speed communication networks operate, and how many physical processes are measured and analyzed.
The Significance of Milliseconds in Technology
The influence of milliseconds on technology is profound and far-reaching. In numerous applications, milliseconds represent the difference between success and failure, smooth operation and disruption, and efficiency and inefficiency. Let's explore some key examples:
1. Computer Processing Power
Computers operate on incredibly short timescales, with processing speeds often measured in gigahertz (GHz), which represent billions of cycles per second. Each of these cycles involves a series of operations that occur within milliseconds or even microseconds (millionths of a second). The speed at which a computer processes data, executes instructions, and renders images is directly influenced by its ability to manage these extremely short time intervals. Improvements in processing power are often measured in terms of reductions in milliseconds required for specific tasks. A faster processor executes instructions in fewer milliseconds, leading to noticeable improvements in performance.
2. Network Latency and Communication
Network latency, the delay in data transmission between two points, is often measured in milliseconds. In online gaming, for example, high latency can result in lag, making the game experience frustrating and unresponsive. Low latency is crucial for real-time applications such as video conferencing and online trading, where delays of even a few milliseconds can be detrimental. High-speed internet connections aim to minimize latency, ensuring fast and efficient communication.
3. High-Frequency Trading (HFT)
In the financial markets, high-frequency trading (HFT) utilizes sophisticated algorithms to execute trades at incredibly high speeds. The ability to execute trades in milliseconds can provide a significant advantage, as even tiny fractions of a second can influence market prices and profitability. HFT firms invest heavily in infrastructure and technology to minimize latency and maximize trading speed, making the precise measurement and management of milliseconds critical to their success.
4. Real-Time Systems and Control
Milliseconds are critical in real-time systems, where the system must respond to events instantaneously. Examples include industrial automation, aircraft control systems, and medical imaging equipment. In these contexts, delays of even a few milliseconds can have severe consequences. Robust and accurate timing mechanisms are crucial to ensure the safe and reliable operation of these systems.
5. Data Acquisition and Signal Processing
In scientific research and engineering, data is often acquired at high sampling rates, often measured in kilohertz (kHz) or megahertz (MHz). This means that thousands or millions of data points are collected per second. Analyzing this massive amount of data requires the precise management of milliseconds, to correctly synchronize and process information accurately. The fidelity of data acquired is closely tied to the precision in timing measurements.
Beyond Milliseconds: Exploring Other Units of Time
Understanding milliseconds necessitates understanding their relationship to other units of time in the metric system:
- Microseconds (µs): One millionth of a second (1 µs = 0.000001 s or 1/1,000,000 s). Used in high-speed electronics and signal processing.
- Nanoseconds (ns): One billionth of a second (1 ns = 0.000000001 s or 1/1,000,000,000 s). Crucial in computer chip design and ultrafast optical communications.
- Picoseconds (ps): One trillionth of a second (1 ps = 0.000000000001 s or 1/1,000,000,000,000 s). Used in atomic and molecular physics.
- Femtoseconds (fs): One quadrillionth of a second (1 fs = 0.000000000000001 s or 1/1,000,000,000,000,000 s). Used in studying ultrafast chemical reactions.
These smaller units demonstrate the incredible precision achievable in modern time measurement technologies. The ability to measure and control time with such accuracy is fundamental to numerous scientific and technological advancements.
The History of Time Measurement and the Second
The journey to accurately measuring milliseconds begins with the definition of the second itself. The definition of the second has evolved over time, reflecting advancements in scientific understanding and technology. Initially, the second was defined as a fraction of the mean solar day. However, the variations in Earth's rotation made this definition imprecise. Later, the second was defined based on the Earth's orbital period.
Modern definitions rely on atomic clocks, which utilize the precise oscillations of cesium atoms to maintain incredibly accurate timekeeping. This atomic definition ensures that the second is consistent and universally applicable. The incredible accuracy of atomic clocks allows for the precise measurement of milliseconds and even smaller units of time, supporting the vast technological advancements we rely on today.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Milliseconds
The seemingly minuscule millisecond holds immense significance in the modern world. From the processing power of computers to the speed of high-frequency trading, from real-time control systems to scientific research, the ability to precisely measure and manage milliseconds is essential. Understanding the relationship between milliseconds and seconds, within the broader context of the metric system and the history of time measurement, underscores the depth and sophistication of our understanding of time and its impact on our technologically advanced society. The continued refinement of timekeeping technologies will undoubtedly further enhance our capabilities in countless fields, making the humble millisecond even more critical in the years to come.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Line Segment Is Drawn In The Figure
Apr 06, 2025
-
16 Is What Percent Of 8
Apr 06, 2025
-
If You Born In 1982 How Old Are You
Apr 06, 2025
-
How To Measure The Pitch Of A Thread
Apr 06, 2025
-
Center And Radius Of A Sphere Calculator
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Milliseconds Are In 1 Second . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
