How Many Seconds Is 1000 Milliseconds
Treneri
Apr 04, 2025 · 5 min read
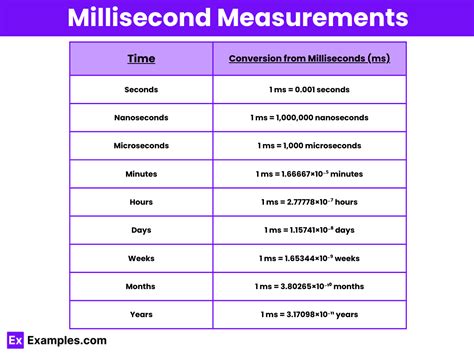
Table of Contents
How Many Seconds is 1000 Milliseconds? A Deep Dive into Time Measurement
The question, "How many seconds is 1000 milliseconds?" might seem trivial at first glance. The answer, one second, is straightforward. However, delving deeper into the topic reveals fascinating insights into the world of time measurement, its history, and its applications in various fields. This article explores the intricacies of milliseconds, seconds, and the broader context of timekeeping, providing a comprehensive understanding for anyone curious about this fundamental unit of measurement.
Understanding the Metric System and its Prefixes
Before jumping into the specifics of milliseconds and seconds, let's establish a firm grasp on the metric system, the foundation upon which these units are built. The metric system, also known as the International System of Units (SI), is a decimal system based on powers of 10. This makes converting between units remarkably simple. The system employs prefixes to denote multiples or fractions of base units. For example:
- Kilo (k): Represents 1000 times the base unit (1 kilometer = 1000 meters).
- Milli (m): Represents 1/1000th of the base unit (1 milliliter = 1/1000th of a liter).
These prefixes are crucial for understanding the relationship between milliseconds and seconds.
The Second: The Foundation of Time Measurement
The second (s) is the base unit of time in the SI system. It's a fundamental unit, meaning it's not defined in terms of other units. Historically, the definition of a second has evolved significantly. Initially, it was based on the Earth's rotation. However, the Earth's rotation isn't perfectly consistent, leading to inaccuracies. Modern definitions rely on atomic clocks, which leverage the incredibly precise oscillations of cesium atoms. This provides an extremely accurate and consistent standard for the second.
Milliseconds: A Thousandth of a Second
A millisecond (ms) is 1/1000th of a second. Using the metric prefix "milli," we can easily understand its relationship to the second. This tiny unit of time is crucial in many applications where high precision and speed are essential.
1000 milliseconds = 1 second
This simple equation encapsulates the core relationship between these two units.
Applications of Milliseconds
The significance of milliseconds becomes apparent when considering its various applications:
-
Computer Science: In the world of computing, milliseconds are critical. Processor speeds, network latency, and data transfer rates are often measured in milliseconds. A difference of a few milliseconds can significantly impact the performance of a computer system or a network.
-
Electronics: Digital electronics relies heavily on milliseconds for timing and synchronization. Many electronic devices operate based on precisely timed events occurring within milliseconds.
-
Physics and Engineering: In fields like physics and engineering, precise time measurements are vital for various experiments and applications. High-speed phenomena, such as laser pulses or chemical reactions, often require measurement in milliseconds or even smaller units like microseconds and nanoseconds.
-
Sports: In sports, particularly those involving speed and precision, milliseconds can make the difference between winning and losing. Timing systems in track and field, swimming, and other sports routinely measure events down to the millisecond.
-
Finance: High-frequency trading in the financial markets relies on incredibly precise timing. Algorithms that execute trades in milliseconds can gain a significant advantage over those with slower response times.
-
Medical Imaging: Medical imaging techniques like MRI and ultrasound rely on precise timing measurements in milliseconds for accurate image reconstruction.
Beyond Milliseconds: Exploring Smaller Units of Time
While milliseconds are incredibly small, even smaller units of time exist and find applications in specific fields:
-
Microseconds (µs): 1/1,000,000th of a second. Used in high-speed electronics and communication systems.
-
Nanoseconds (ns): 1/1,000,000,000th of a second. Crucial in fields like telecommunications, computing, and atomic physics.
-
Picoseconds (ps): 1/1,000,000,000,000th of a second. Used in ultra-fast laser technology and research involving light and matter interactions.
The Importance of Accurate Time Measurement
Accurate time measurement is fundamental to countless aspects of modern life. From the global positioning system (GPS) that relies on precisely synchronized atomic clocks to the intricate timing mechanisms within our computers and smartphones, the ability to measure time accurately with high precision is paramount. The simple conversion of 1000 milliseconds to 1 second underpins much of this technological marvel.
Historical Context of Time Measurement
Understanding the history of time measurement provides a deeper appreciation for the sophistication of modern timekeeping. Early methods were crude, relying on the observation of celestial bodies. The sundial, water clock, and hourglass were among the earliest tools used to measure time. The development of mechanical clocks and later, quartz and atomic clocks, revolutionized timekeeping, enabling increasingly precise measurements.
Practical Applications: Examples of Millisecond Precision
Let's illustrate the practical significance of milliseconds with a few examples:
Example 1: Network Latency: Imagine you're playing an online video game. A network latency of 100 milliseconds might seem insignificant, but it can translate to a noticeable delay in your actions being registered by the game server. This delay can be the difference between victory and defeat in a fast-paced game.
Example 2: Financial Transactions: High-frequency trading algorithms operate at speeds measured in microseconds and milliseconds. A difference of a few milliseconds in the execution time of a trade can result in substantial financial gains or losses. The precise timing of these transactions is crucial for success in this highly competitive field.
Example 3: Medical Imaging: In medical imaging, precise timing is essential for creating clear and accurate images. The timing of ultrasound pulses and the acquisition of data in MRI scans are crucial for successful diagnosis and treatment. Even minor variations in timing can affect the quality of the images produced.
Example 4: Data Acquisition: In scientific research, experiments often involve collecting large amounts of data over short periods. The precise timing of data acquisition is critical for accurate analysis and interpretation of experimental results.
Conclusion: The Ubiquitous Millisecond
In conclusion, while the answer to "How many seconds is 1000 milliseconds?" is simply one second, the significance of this unit extends far beyond this basic conversion. Milliseconds are crucial in various technological and scientific fields, highlighting the importance of precise time measurement in our increasingly interconnected world. From the intricacies of computer processing to the precision of medical imaging, milliseconds are a fundamental unit that underpins much of modern technology and scientific advancement. Understanding the relationship between milliseconds and seconds, therefore, is not just a matter of simple arithmetic but also a window into the world of precise time measurement and its far-reaching implications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
2 Cups Dry Macaroni Equals How Much Cooked
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Much Is 15 Ml In Tablespoons
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Miles Is 8200 Steps
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Seconds Is 1000 Milliseconds . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
