How Many Seconds Is In A Hour
Treneri
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
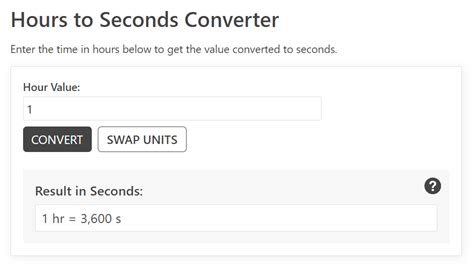
Table of Contents
How Many Seconds Are in an Hour? A Comprehensive Exploration of Time Measurement
Knowing how many seconds are in an hour is fundamental to understanding time. While seemingly simple, this seemingly basic question opens a door to a fascinating exploration of timekeeping, its history, and its significance in various aspects of our lives. This comprehensive guide will not only answer the question directly but also delve into the broader context of time measurement and its relevance in various fields.
The Simple Answer: 3600 Seconds
The short answer is straightforward: there are 3600 seconds in one hour. This is a universally accepted fact based on the standard system of time measurement.
Understanding the Calculation
The calculation is derived from the fundamental units of time:
- 60 seconds = 1 minute
- 60 minutes = 1 hour
Therefore, to find the number of seconds in an hour, we multiply the number of seconds in a minute by the number of minutes in an hour:
60 seconds/minute * 60 minutes/hour = 3600 seconds/hour
This simple calculation forms the basis for numerous time-related calculations across various disciplines.
The History of Time Measurement: A Journey Through Centuries
Our current system of time measurement has evolved over millennia. Early civilizations relied on observable celestial events, such as the rising and setting of the sun, the phases of the moon, and the apparent movement of stars, to track time. These observations led to the development of various calendars and timekeeping devices.
Ancient Timekeeping: Sun Dials and Water Clocks
Ancient Egyptians, Greeks, and Romans developed sophisticated sun dials and water clocks, providing more accurate measurements of time than simply observing the sun's position. These early devices laid the groundwork for more complex timekeeping systems.
The Invention of the Mechanical Clock: A Revolution in Accuracy
The invention of the mechanical clock in the medieval period marked a significant leap forward in timekeeping accuracy. These clocks, powered by weights and gears, allowed for more precise measurement of shorter intervals of time, paving the way for the standardization of the second, minute, and hour as we know them.
The Development of the Atomic Clock: Achieving Unprecedented Precision
The development of the atomic clock in the 20th century revolutionized timekeeping. By utilizing the precise vibrations of atoms, atomic clocks provide an unprecedented level of accuracy, crucial for scientific research, navigation systems (like GPS), and global time synchronization.
The Significance of Seconds in Various Fields
The seemingly small unit of a second holds immense significance across various disciplines. Its precise measurement is crucial for accurate and reliable functioning in many areas:
Science and Technology: Precision and Accuracy
In science and technology, the precise measurement of seconds is critical for experiments, data analysis, and technological applications. High-precision timing is essential in fields such as:
- Physics: Experiments involving high-speed phenomena, such as particle physics and nuclear reactions, rely on incredibly precise time measurements.
- Astronomy: Observing celestial events and studying the movement of celestial bodies requires accurate timing to correlate observations.
- Engineering: The synchronization of complex systems, such as communication networks and power grids, depends on precisely synchronized clocks.
- Medicine: Medical imaging techniques, such as electrocardiograms (ECGs) and electroencephalograms (EEGs), rely on precise time measurements to capture physiological signals.
Everyday Life: Scheduling and Organization
While we may not always consciously think about it, seconds play a crucial role in our daily lives, influencing our scheduling and organization:
- Scheduling appointments: We schedule appointments down to the minute, which are further broken down into seconds.
- Project management: Project timelines are often broken down into seconds to track progress and allocate resources efficiently.
- Sports and competitions: Many sports depend on precise time measurements, such as track and field events, swimming competitions, and even video games.
Finance and Trading: Speed and Efficiency
In the world of finance and trading, milliseconds and even microseconds can make a significant difference. High-frequency trading algorithms rely on extremely fast processing speeds to execute trades in fractions of a second. The precise measurement of time is crucial for accurate record-keeping and regulatory compliance.
Beyond the Second: Exploring Different Units of Time
While the second is a fundamental unit, other units of time are used to measure longer and shorter durations:
- Milliseconds (ms): One-thousandth of a second (1/1000 s)
- Microseconds (µs): One-millionth of a second (1/1,000,000 s)
- Nanoseconds (ns): One-billionth of a second (1/1,000,000,000 s)
- Days: 24 hours
- Weeks: 7 days
- Months: Approximately 30 or 31 days
- Years: 365 days (or 366 in a leap year)
- Decades: 10 years
- Centuries: 100 years
- Millennia: 1000 years
Understanding the relationship between these units is crucial for working with various time scales.
Time Zones and Coordinated Universal Time (UTC)
Due to the Earth's rotation, different parts of the world experience different times simultaneously. To address this, time zones were established, creating standardized time across geographical regions. Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), formerly known as Greenwich Mean Time (GMT), serves as the primary reference for coordinating time worldwide.
UTC is crucial for global communication, coordination of events, and the synchronization of computer systems and networks across different time zones.
Leap Seconds: Adjusting for the Earth's Irregular Rotation
The Earth's rotation is not perfectly uniform; it gradually slows down over time. To compensate for these variations, leap seconds are occasionally added to Coordinated Universal Time (UTC) to keep it aligned with astronomical time. These adjustments ensure that the time reported by atomic clocks remains synchronized with the Earth's rotation.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Seconds
The seemingly simple question of how many seconds are in an hour opens up a wealth of information about time measurement, its history, and its multifaceted applications in modern society. From the ancient sun dials to the highly accurate atomic clocks, the quest for precise timekeeping has driven technological advancements and continues to be crucial for numerous scientific, technological, and everyday applications. The humble second, a fundamental unit of time, remains an essential element in our understanding and experience of the world around us. Understanding its significance and its relationship to other units of time is vital for numerous aspects of modern life.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Thick Is 30 Mil In Inches
Apr 06, 2025
-
Formula For Change In Potential Energy
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Long Until 4 45 Am
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Cups Is 2 Gallons Of Water
Apr 06, 2025
-
8 Square Feet Is How Big
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Seconds Is In A Hour . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
