How To Calculate Diameter Of A Cylinder
Treneri
Apr 03, 2025 · 5 min read
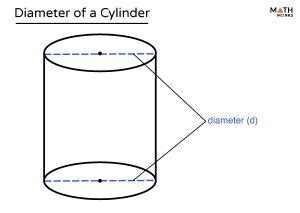
Table of Contents
- How To Calculate Diameter Of A Cylinder
- Table of Contents
- How to Calculate the Diameter of a Cylinder: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding Cylindrical Geometry
- Method 1: Measuring the Diameter Directly
- Method 2: Calculating Diameter from the Radius
- Method 3: Calculating Diameter from the Circumference
- Method 4: Calculating Diameter from the Cylinder's Volume and Height
- Method 5: Using Indirect Measurements and Similar Triangles
- Method 6: Using Advanced Techniques (for Complex Scenarios)
- Error Analysis and Minimizing Uncertainty
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
How to Calculate the Diameter of a Cylinder: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the diameter of a cylinder is a fundamental task in various fields, from engineering and manufacturing to everyday problem-solving. Whether you're working with pipes, tanks, or even simple cylindrical objects, knowing how to accurately calculate the diameter is crucial. This comprehensive guide will explore different methods for calculating the diameter of a cylinder, catering to various scenarios and levels of available information. We'll delve into the underlying principles, provide step-by-step instructions, and offer practical examples to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Cylindrical Geometry
Before we dive into the calculations, let's establish a clear understanding of the key components of a cylinder. A cylinder is a three-dimensional geometric shape with two parallel circular bases connected by a curved surface. The key dimensions are:
- Diameter: The distance across the circle, passing through the center. This is the value we'll be focusing on calculating.
- Radius: Half the diameter. It's the distance from the center of the circle to any point on the circumference.
- Height (or Length): The distance between the two circular bases. This dimension is often irrelevant when solely calculating the diameter.
- Circumference: The distance around the circle. This is related to the diameter through the formula: Circumference = π * Diameter.
Understanding these relationships is fundamental to applying the different calculation methods.
Method 1: Measuring the Diameter Directly
The simplest and often most accurate method is direct measurement. If you have physical access to the cylinder, you can use tools like:
- Calipers: These precision instruments are ideal for accurate diameter measurement. Simply position the jaws of the caliper across the widest part of the cylinder and read the measurement. Digital calipers offer even greater precision.
- Ruler: For less precise measurements, a ruler can be used. Place the cylinder on a flat surface and carefully measure the distance across its widest part. Ensure the ruler is perpendicular to the cylinder's axis.
- Measuring Tape: A flexible measuring tape can be useful for measuring the circumference. Once you have the circumference, you can calculate the diameter using the formula: Diameter = Circumference / π (where π ≈ 3.14159).
Important Considerations for Direct Measurement:
- Accuracy: The accuracy of your measurement depends heavily on the precision of your measuring instrument. Calipers are generally preferred for greater accuracy.
- Accessibility: Direct measurement requires physical access to the cylinder. This method won't be feasible if you only have indirect information about the cylinder's dimensions.
- Surface Irregularities: Surface imperfections or irregularities can affect the accuracy of the measurement. Take multiple measurements at different points and average them to minimize errors.
Method 2: Calculating Diameter from the Radius
If you know the radius of the cylinder, calculating the diameter is straightforward:
Diameter = 2 * Radius
This is a fundamental geometric relationship. Simply multiply the radius by two to obtain the diameter. For example, if the radius is 5 cm, the diameter is 2 * 5 cm = 10 cm.
Method 3: Calculating Diameter from the Circumference
If you only know the circumference of the cylinder, you can use the following formula:
Diameter = Circumference / π
Where π (pi) is approximately 3.14159. Remember that this calculation assumes a perfectly circular base. Any deviation from a perfect circle will introduce error.
Example: If the circumference of a cylinder is 31.4 cm, the diameter is 31.4 cm / 3.14159 ≈ 10 cm.
This method is particularly useful when dealing with curved objects where measuring the diameter directly is difficult.
Method 4: Calculating Diameter from the Cylinder's Volume and Height
This method is slightly more complex and requires knowing both the volume and the height of the cylinder. The formula for the volume of a cylinder is:
Volume = π * Radius² * Height
To find the diameter, we need to rearrange the formula to solve for the radius, and then double the radius to get the diameter.
- Solve for Radius: Radius = √(Volume / (π * Height))
- Calculate Diameter: Diameter = 2 * Radius
Example: Let's say the volume of a cylinder is 1570 cubic cm and its height is 10 cm.
- Radius = √(1570 cm³ / (3.14159 * 10 cm)) ≈ √(50 cm²) ≈ 7 cm
- Diameter = 2 * 7 cm = 14 cm
This method is useful when dealing with situations where direct measurement or circumference measurement is not practical.
Method 5: Using Indirect Measurements and Similar Triangles
In some cases, you might not be able to directly measure the cylinder, but you might have information about a similar object or a scaled representation. Similar triangles can help in these situations. If you have a scale drawing or model of the cylinder, measure the relevant dimensions on the model, and use the scale factor to calculate the actual diameter. For example, if a scale model has a diameter of 2 cm and the scale is 1:10, the actual diameter is 2 cm * 10 = 20 cm.
Method 6: Using Advanced Techniques (for Complex Scenarios)
For highly irregular cylinders or situations where extreme precision is required, advanced techniques might be necessary. These could include:
- 3D Scanning: This technology creates a detailed digital model of the cylinder, from which accurate diameter measurements can be extracted.
- Image Processing: Sophisticated image analysis techniques can be used to extract dimensional information from images of the cylinder.
- Laser Measurement: Laser-based measurement systems offer highly accurate and non-contact measurements of cylindrical objects.
Error Analysis and Minimizing Uncertainty
No matter which method you choose, it's crucial to consider potential sources of error and uncertainty. Factors influencing accuracy include:
- Instrument Precision: The accuracy of your measuring instrument directly impacts the accuracy of your results.
- Measurement Technique: Proper measurement techniques are essential to minimize human error.
- Environmental Factors: Temperature and humidity can affect the dimensions of certain materials.
- Cylinder Irregularities: Imperfections in the cylinder's shape will affect the accuracy of the measurement.
To minimize error:
- Use high-quality measuring instruments.
- Take multiple measurements and calculate the average.
- Consider the limitations of your chosen method.
- Document your methodology and uncertainties.
Conclusion
Calculating the diameter of a cylinder is a fundamental skill with applications across many disciplines. This guide has provided several methods, ranging from simple direct measurement to more complex calculations based on volume and indirect measurements. By understanding the principles involved and considering potential sources of error, you can accurately determine the diameter of a cylinder in various real-world scenarios. Remember to choose the most appropriate method based on the information available and the required level of accuracy. Always strive for precision and meticulousness in your measurements and calculations to ensure reliable results.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Grade Is A 28 Out Of 40
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Fast Is A 4 Hour Marathon
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Grade Is A 60 Out Of 100
Apr 06, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 13 Libras En Kilos
Apr 06, 2025
-
Used Car Sales Tax In Ohio
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Calculate Diameter Of A Cylinder . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
