How To Calculate Pipe Volume Formula
Treneri
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
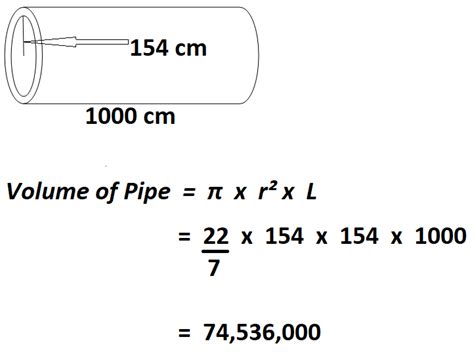
Table of Contents
How to Calculate Pipe Volume: A Comprehensive Guide
Calculating the volume of a pipe, also known as a cylinder, is a fundamental task in various fields, including engineering, construction, and plumbing. Understanding how to perform this calculation accurately is crucial for tasks ranging from estimating material costs to designing efficient fluid systems. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the process, exploring different scenarios and providing practical examples.
Understanding the Basics: Pipe Dimensions and Formula
Before diving into the calculations, let's define the key dimensions of a pipe:
- Length (L): The total length of the pipe, measured in consistent units (e.g., meters, feet, inches).
- Outer Diameter (OD): The diameter of the pipe measured from the outermost point on one side to the outermost point on the opposite side.
- Inner Diameter (ID): The diameter of the pipe's hollow interior, measured from the innermost point on one side to the innermost point on the opposite side.
- Wall Thickness (WT): The difference between the outer diameter and the inner diameter (OD - ID) / 2.
The fundamental formula for calculating the volume of a cylinder (and therefore a pipe) is:
Volume = π * r² * h
Where:
- π (pi): A mathematical constant, approximately equal to 3.14159.
- r: The radius of the cylinder (half of the diameter).
- h: The height of the cylinder (in the case of a pipe, this is the length).
However, since pipes are hollow, we need to adjust this formula to account for the empty space inside. We'll calculate the volume of the outer cylinder and subtract the volume of the inner cylinder.
Calculating the Volume of a Hollow Pipe: The Complete Formula
To calculate the volume of the material that makes up the pipe itself (excluding the hollow interior), we use the following formula:
Volume = π * [(OD/2)² - (ID/2)²] * L
This formula accounts for the annular cross-section of the pipe. Let's break it down:
- π * (OD/2)²: Calculates the area of the outer circle.
- π * (ID/2)²: Calculates the area of the inner circle.
- [(OD/2)² - (ID/2)²]: Finds the difference between the outer and inner circle areas, representing the cross-sectional area of the pipe material.
- L: Multiplies the cross-sectional area by the length to obtain the total volume.
Step-by-Step Calculation with Example
Let's work through a practical example. Consider a steel pipe with the following dimensions:
- Outer Diameter (OD): 10 centimeters (cm)
- Inner Diameter (ID): 8 centimeters (cm)
- Length (L): 5 meters (m) (Remember to convert all units to be consistent!)
Step 1: Convert Units to a Consistent System
Since the length is given in meters and the diameters in centimeters, it's crucial to maintain consistency. Let's convert everything to centimeters:
- OD: 10 cm
- ID: 8 cm
- L: 500 cm (5 meters * 100 centimeters/meter)
Step 2: Apply the Formula
Substitute the values into the formula:
Volume = π * [(10/2)² - (8/2)²] * 500
Volume = π * [5² - 4²] * 500
Volume = π * [25 - 16] * 500
Volume = π * 9 * 500
Volume ≈ 14137.17 cubic centimeters (cm³)
Step 3: Convert to More Practical Units (Optional)
Cubic centimeters might not be the most practical unit for larger pipes. You can convert the volume to liters (1 liter = 1000 cubic centimeters) or cubic meters (1 cubic meter = 1,000,000 cubic centimeters):
Volume ≈ 14.14 liters
Volume ≈ 0.01414 cubic meters
Calculating Volume Using Only Outer Diameter and Wall Thickness
If you only know the outer diameter and wall thickness, you can easily derive the inner diameter and then use the previous formula.
Inner Diameter (ID) = OD - 2 * WT
Once you have the inner diameter, follow the steps outlined above.
Dealing with Different Pipe Shapes and Irregularities
While the above calculations are accurate for perfectly cylindrical pipes, real-world scenarios can present complexities:
- Tapered Pipes: If the pipe's diameter changes along its length (tapered), you'll need to use calculus (integration) for an accurate volume calculation. Approximations can be made by dividing the pipe into sections and treating each section as a cylinder.
- Bent Pipes: Bending the pipe doesn't change its volume, provided no material is added or removed during the bending process.
- Imperfect Cylinders: Minor irregularities in the pipe's shape will introduce small errors into the calculation. These errors are usually negligible for most practical purposes.
- Elliptical Pipes: For pipes with elliptical cross-sections, the formula becomes more complex, involving the semi-major and semi-minor axes of the ellipse.
Practical Applications and Importance of Accurate Calculations
Accurate pipe volume calculations are essential in various applications:
- Material Estimation: Determining the amount of material required for pipe manufacturing or construction projects.
- Fluid Flow Calculations: Knowing the internal volume is crucial for calculating flow rates and pressures in pipelines.
- Cost Estimation: Accurate volume calculations help in estimating material costs and project budgeting.
- Inventory Management: Tracking the amount of liquid or gas stored in pipelines for efficient inventory management.
- Civil and Environmental Engineering: In tasks such as designing drainage systems, water supply networks, and irrigation systems.
Advanced Considerations and Tools
For more complex pipe geometries or large-scale projects, using specialized software or computer-aided design (CAD) tools is recommended. These tools can handle complex calculations, handle variations in pipe dimensions, and provide detailed visualizations.
Conclusion: Mastering Pipe Volume Calculations
Mastering the calculation of pipe volume is a valuable skill in various disciplines. By understanding the fundamental formula and its variations, you can accurately determine the volume of pipe material and efficiently manage resources. Remember to always maintain unit consistency throughout your calculations and consider using specialized tools for complex scenarios. Accurate calculations are crucial for ensuring the success and efficiency of any project involving pipes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Grade Is A 28 Out Of 40
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Fast Is A 4 Hour Marathon
Apr 06, 2025
-
What Grade Is A 60 Out Of 100
Apr 06, 2025
-
Cuanto Es 13 Libras En Kilos
Apr 06, 2025
-
Used Car Sales Tax In Ohio
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Calculate Pipe Volume Formula . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
