Is Uv 7 Good For Tanning
Treneri
Apr 07, 2025 · 5 min read
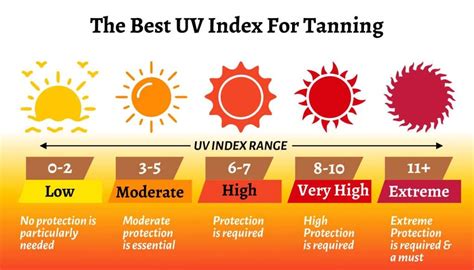
Table of Contents
- Is Uv 7 Good For Tanning
- Table of Contents
- Is UV 7 Good for Tanning? Understanding UV Rays and Safe Sun Exposure
- Understanding the UV Spectrum
- The Role of UVA and UVB in Tanning
- The Dangers of Excessive UV Exposure
- Safer Alternatives to Tanning
- Protecting Your Skin from the Sun
- Conclusion: Prioritize Skin Health
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Is UV 7 Good for Tanning? Understanding UV Rays and Safe Sun Exposure
The pursuit of a sun-kissed glow is a common desire, leading many to explore various methods for achieving a tan. UV 7, often mentioned in tanning discussions, refers to a specific wavelength within the ultraviolet (UV) spectrum. However, the question of whether UV 7 is "good" for tanning is complex and requires a nuanced understanding of UV radiation and its effects on the skin. This article will delve into the science behind UV rays, the role of UV 7 in tanning, the risks associated with UV exposure, and safer alternatives for achieving a bronzed complexion.
Understanding the UV Spectrum
Sunlight comprises various wavelengths of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light and invisible UV radiation. The UV spectrum is further divided into three categories:
- UVA (Ultraviolet A): These rays have longer wavelengths and penetrate deeper into the skin, contributing to aging and wrinkles. They are also responsible for immediate tanning.
- UVB (Ultraviolet B): These rays have shorter wavelengths and are primarily responsible for sunburn. They also play a role in tanning, albeit indirectly by stimulating melanin production.
- UVC (Ultraviolet C): These rays are the shortest and most harmful, but are largely absorbed by the Earth's ozone layer. They don't significantly contribute to tanning or sun damage at ground level.
The term "UV 7" doesn't represent a specific, clearly defined band within the UV spectrum used in scientific literature. It's likely a colloquial reference, possibly related to a specific tanning bed or sunlamp's output, or a misunderstanding of the broader UV spectrum. To accurately discuss the effects on tanning, we need to consider the entire UV spectrum and its components, rather than an undefined "UV 7."
The Role of UVA and UVB in Tanning
Tanning is the skin's natural defense mechanism against harmful UV radiation. When exposed to UV rays, the skin produces melanin, a pigment that absorbs UV radiation and protects the deeper layers of the skin from damage.
- UVA and immediate tanning: UVA rays cause immediate tanning by stimulating melanin dispersion within the skin. This tan is often superficial and fades quickly.
- UVB and delayed tanning: UVB rays, while causing sunburn, also trigger the production of new melanin, leading to a deeper and longer-lasting tan. However, this process involves skin damage, making it a risky way to achieve a tan.
It's crucial to understand that tanning, regardless of its source, is a sign of skin damage. The skin is reacting to UV-induced injury by producing melanin to protect itself. This damage contributes to premature aging, wrinkles, and increases the risk of skin cancer.
The Dangers of Excessive UV Exposure
Exposure to excessive UV radiation, whether from natural sunlight or artificial sources like tanning beds, poses significant health risks:
- Sunburn: This is the most immediate effect of UVB exposure, characterized by redness, pain, and inflammation. Severe sunburn can lead to blistering and peeling.
- Premature Aging: Both UVA and UVB rays contribute to premature aging, resulting in wrinkles, age spots, and loss of skin elasticity. This process is accelerated by repeated sun exposure.
- Skin Cancer: This is the most serious long-term risk of UV exposure. Excessive exposure significantly increases the risk of basal cell carcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, the deadliest form of skin cancer. The damage caused by UV radiation accumulates over time, so even seemingly minor sunburns can contribute to the risk.
- Eye Damage: UV radiation can damage the eyes, leading to cataracts, macular degeneration, and photokeratitis (sunburn of the cornea).
Safer Alternatives to Tanning
Given the significant health risks associated with UV exposure, seeking a tan through sunbathing or tanning beds is strongly discouraged. Fortunately, several safer alternatives exist for achieving a sun-kissed look:
- Self-Tanning Products: These lotions, creams, and sprays contain dihydroxyacetone (DHA), a chemical that reacts with the amino acids in the skin's surface to produce a temporary brown color. Self-tanners offer a safe and convenient way to achieve a tan without the risks of UV exposure. Choose reputable brands and follow instructions carefully for optimal results.
- Bronzing Makeup: Makeup products like bronzers and powders can create a sun-kissed appearance without the need for UV exposure. These products provide a temporary tan that can be adjusted according to preference.
- Spray Tanning: Professional spray tanning involves applying a DHA-based solution to the skin using a specialized spray gun. This method can provide a more even and natural-looking tan than self-tanning lotions. Choose a reputable salon that uses high-quality products and adheres to safety standards.
Protecting Your Skin from the Sun
Even when not intentionally tanning, it's crucial to protect your skin from harmful UV rays. Follow these sun safety tips:
- Seek Shade: Limit your time in direct sunlight, especially during peak hours (10 a.m. to 4 p.m.).
- Wear Protective Clothing: Wear long sleeves, long pants, and a wide-brimmed hat to cover exposed skin.
- Use Sunscreen: Apply a broad-spectrum sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher to all exposed skin, even on cloudy days. Reapply every two hours, or more frequently if swimming or sweating.
- Wear Sunglasses: Protect your eyes from UV radiation by wearing sunglasses that block 99-100% of UVA and UVB rays.
Conclusion: Prioritize Skin Health
While the desire for a tan is understandable, it's paramount to prioritize skin health. The idea that "UV 7" or any specific UV wavelength is "good" for tanning is misleading. All UV radiation poses risks, and excessive exposure can lead to serious health consequences. Embrace safer alternatives like self-tanners, bronzing makeup, and spray tanning to achieve a sun-kissed glow without compromising your skin's health. Remember that a healthy, radiant complexion is far more attractive than a tan acquired at the expense of your long-term well-being. Always practice safe sun habits to minimize your risk of sun damage and skin cancer. Consult a dermatologist for personalized advice on sun protection and skin care.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Gallons Are In A Swimming Pool
Apr 14, 2025
-
How To Calculate Rent Per Square Foot Per Month
Apr 14, 2025
-
How Many Hours Is 29 Days
Apr 14, 2025
-
2 Km Is How Many Steps
Apr 14, 2025
-
Common Multiples Of 16 And 18
Apr 14, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Uv 7 Good For Tanning . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.