How Many Inches Of Snow Equals Inches Of Rain
Treneri
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
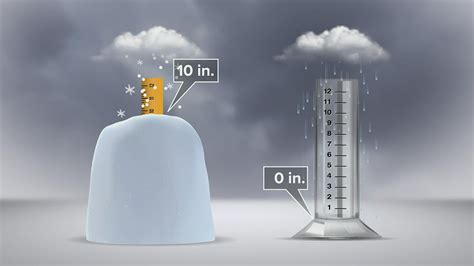
Table of Contents
How Many Inches of Snow Equals Inches of Rain? A Comprehensive Guide
The question, "How many inches of snow equals inches of rain?" is a common one, especially during winter storms. The answer, however, isn't a simple one-to-one ratio. The conversion depends heavily on several factors, making it a complex meteorological calculation rather than a straightforward mathematical equation. Understanding these nuances is crucial for accurately assessing the impact of snowfall and comparing it to rainfall.
The Variable Nature of Snow-to-Rain Ratios
The ratio of snow to rain isn't constant; it fluctuates dramatically depending on a multitude of atmospheric conditions. These factors significantly influence the density of the snow, which is the key to accurate conversion. A fluffy, powdery snow will have a much lower density than wet, heavy snow. This means that a given volume of fluffy snow will contain far less water than the same volume of wet snow.
Factors Affecting Snow Density:
-
Temperature: Colder temperatures generally produce lighter, drier snow with a lower density. Warmer temperatures, closer to freezing, often result in wetter, denser snow.
-
Humidity: High humidity contributes to the formation of wetter snow, increasing its density. Low humidity leads to drier, fluffier snow with a lower density.
-
Wind: Strong winds can pack snow, increasing its density. Calm conditions often result in lighter, less compacted snow.
-
Snow Type: Different types of snow, such as snowflakes, snow pellets (graupel), or ice crystals, have varying densities. Ice crystals, for example, will be denser than snowflakes.
The Common (but Inaccurate) 10:1 Ratio
You'll often hear the rule of thumb that 10 inches of snow is equivalent to 1 inch of rain. While this is a widely circulated approximation, it's highly inaccurate in many cases. It might hold true for certain types of snow under specific conditions, but it shouldn't be relied upon for precise measurements. Using this ratio can lead to significant underestimation or overestimation of the actual water content in snowfall, potentially resulting in inaccurate flood predictions, inadequate infrastructure preparation, and misjudgments regarding the severity of winter storms.
A More Accurate Approach: Understanding Snow Water Equivalent (SWE)
The most reliable method for determining the water content of snow is to measure its Snow Water Equivalent (SWE). SWE represents the depth of water that would result if a given amount of snow were melted. This is often expressed in inches or millimeters. To determine the SWE, specialized equipment is usually used, such as a snow pillow or snow course. However, even without specialized equipment, we can make better estimations than the 10:1 ratio by considering the factors mentioned earlier.
Estimating SWE: Observational Clues
While precise SWE measurements require scientific instruments, you can make a more informed estimate by considering the snow's characteristics:
-
Powdery Snow: This type of snow is light and fluffy. It might have a snow-to-water ratio of 15:1 or even higher.
-
Wet, Heavy Snow: This type of snow is denser and compresses more easily. Its snow-to-water ratio might be closer to 5:1 or even lower.
-
Slushy Snow: This is the snowpack that is almost melted. The ratio might be between 2:1 and 4:1.
By visually assessing the snow's texture and weight, you can arrive at a more reasonable estimate than the generalized 10:1 ratio.
The Importance of Accurate Snow-to-Rain Conversions
Accurate conversions from snow to rain are essential for various applications:
-
Flood Prediction: Heavy snowfall can lead to significant flooding, particularly when rapid melting occurs. Accurate SWE measurements are crucial for predicting potential flood risks.
-
Water Resource Management: Snowpack acts as a natural reservoir, providing a crucial source of water for downstream ecosystems and human consumption. Precise SWE estimations are vital for managing water resources effectively.
-
Infrastructure Planning: Engineers and urban planners need accurate snow data to design and maintain infrastructure that can withstand the weight and impact of heavy snowfall.
-
Agriculture: Snowpack is a critical factor influencing agricultural yields. Accurate snow measurements help farmers make informed decisions about crop planning and irrigation.
-
Weather Forecasting: Accurate snow-to-water ratios are important for weather forecasters to provide precise predictions of precipitation amounts. This information is essential for public safety and preparedness.
Beyond the Inches: Considering Other Factors
While focusing on inches of snow and rain provides a useful comparison, it's crucial to remember the broader context. The impact of snowfall extends beyond just the water content:
-
Snow Density and Weight: The sheer weight of heavy snow can cause structural damage to buildings, power lines, and trees.
-
Visibility: Snowstorms drastically reduce visibility, leading to hazardous driving conditions and disruptions to transportation.
-
Wind Chill: The combination of cold temperatures and wind can cause hypothermia and frostbite.
-
Avalanche Risk: In mountainous regions, heavy snowfall increases the risk of avalanches, posing a significant threat to life and property.
Conclusion: No Single Answer, but Informed Estimation is Key
There is no single, universally applicable answer to the question of how many inches of snow equal inches of rain. The 10:1 ratio is a rough approximation that can be significantly inaccurate. A more accurate approach requires considering the various factors influencing snow density and employing the concept of Snow Water Equivalent (SWE). By visually assessing the snow's characteristics and understanding the limitations of generalized ratios, individuals can make more informed estimations of the water content within a snowpack. This understanding is crucial for safety, resource management, and accurate weather forecasting. Accurate assessment of snow-to-rain ratios is not merely an academic exercise; it is vital for effective planning, safety, and preparedness during winter storms.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
90 Days From July 17 2024
Apr 06, 2025
-
Least Common Denominator Of 8 And 4
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Many Ounces Is 11 Cups
Apr 06, 2025
-
How Long Ago Was 500 Bc
Apr 06, 2025
-
7 X To The Power Of 5
Apr 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Inches Of Snow Equals Inches Of Rain . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
