What Is The Percent Of Change From 8 To 10
Treneri
May 12, 2025 · 5 min read
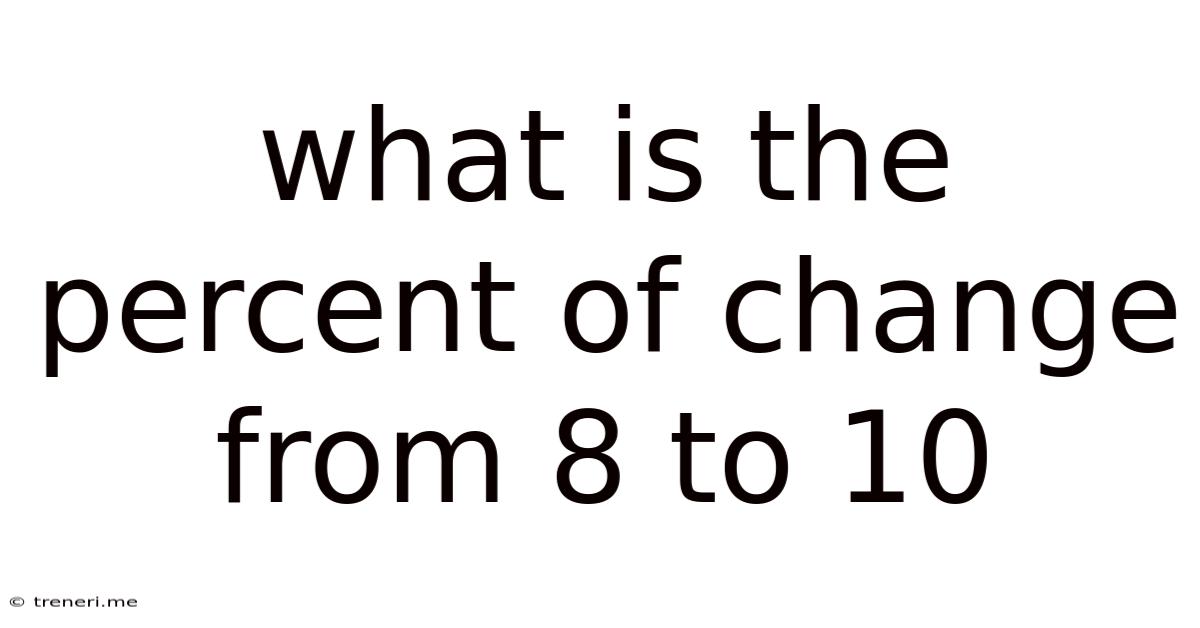
Table of Contents
What is the Percent of Change from 8 to 10? A Comprehensive Guide
Calculating percentage change is a fundamental skill with wide-ranging applications in various fields, from finance and economics to science and everyday life. Understanding how to calculate percentage change allows you to analyze trends, compare data points, and make informed decisions. This article will delve into the process of determining the percentage change from 8 to 10, providing a detailed explanation, various approaches, and practical examples to solidify your understanding. We'll also explore related concepts and address common misconceptions.
Understanding Percentage Change
Percentage change represents the relative difference between an initial value and a final value, expressed as a percentage. It indicates the extent to which a value has increased or decreased over time or compared to a benchmark. The formula is straightforward, yet its application can be nuanced depending on the context.
The Basic Formula:
Percentage Change = [(New Value - Old Value) / Old Value] x 100%
Key Terms:
- Old Value: The initial value or the starting point. In our example, the old value is 8.
- New Value: The final value or the ending point. In our example, the new value is 10.
Calculating the Percentage Change from 8 to 10
Let's apply the formula to calculate the percentage change from 8 to 10:
-
Find the difference: Subtract the old value from the new value: 10 - 8 = 2
-
Divide the difference by the old value: 2 / 8 = 0.25
-
Multiply by 100%: 0.25 x 100% = 25%
Therefore, the percentage change from 8 to 10 is 25%. This indicates a 25% increase because the new value is larger than the old value.
Different Scenarios and Interpretations
While the basic formula is consistent, the interpretation and application can vary depending on the context. Let's explore some scenarios:
Scenario 1: Positive Percentage Change (Increase)
When the new value is greater than the old value, the percentage change will be positive, representing an increase. This is the case in our example (8 to 10). The result, 25%, signifies a 25% increase. This is frequently used to track growth in sales, profits, populations, or any other metric that tends to increase over time.
Scenario 2: Negative Percentage Change (Decrease)
If the new value is smaller than the old value, the percentage change will be negative, representing a decrease. For example, if the value decreased from 10 to 8, the calculation would be:
(8 - 10) / 10 x 100% = -20%
This indicates a 20% decrease. Negative percentage changes are vital for analyzing factors like declining profits, shrinking populations, or reductions in resource consumption.
Scenario 3: Zero Percentage Change (No Change)
If the new value is the same as the old value, the percentage change will be 0%. This indicates no change. For example, if a value remains at 8, the percentage change is 0%. This is a crucial benchmark for comparison and helps identify periods of stability or stagnation.
Practical Applications of Percentage Change
Understanding percentage change is crucial in many areas:
Finance and Investing:
- Stock Market Performance: Tracking the percentage change in stock prices over time helps investors assess investment performance.
- Return on Investment (ROI): Calculating the percentage change in investment value helps determine the profitability of an investment.
- Inflation: Tracking the percentage change in the price index measures inflation and its impact on purchasing power.
- Interest Rates: Percentage change is used to calculate compound interest and the effective annual rate of returns.
Business and Economics:
- Sales Growth: Analyzing percentage changes in sales figures helps businesses understand growth trends.
- Profitability Analysis: Tracking percentage changes in profits allows businesses to assess their financial health.
- Economic Indicators: Percentage changes in GDP, unemployment rates, and other economic indicators provide insights into the overall economy.
Science and Engineering:
- Experimental Results: Percentage change is used to compare experimental results and quantify changes in variables.
- Data Analysis: Percentage change is a standard tool for analyzing data and identifying trends in scientific research.
Everyday Life:
- Budgeting: Tracking percentage changes in spending habits helps individuals manage their finances more effectively.
- Shopping: Comparing prices and determining percentage discounts helps consumers make informed purchasing decisions.
- Personal Fitness: Tracking percentage changes in weight or other fitness metrics allows individuals to monitor their progress.
Advanced Concepts and Considerations
While the basic formula is sufficient for many scenarios, some situations might require more advanced considerations:
Compound Percentage Change:
When dealing with multiple percentage changes over time, the simple addition of percentages can be misleading. Instead, compound percentage change should be calculated to accurately reflect the cumulative effect. For example, a 10% increase followed by a 10% decrease doesn't result in a net change of 0%.
Weighted Averages:
In some cases, different values might carry different weights. For instance, if you're calculating the percentage change in your investment portfolio, different assets might have different weights based on their proportion in the portfolio. In such cases, weighted average percentage change should be used.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Several common mistakes can lead to inaccurate calculations:
- Incorrect Order of Subtraction: Always subtract the old value from the new value to avoid incorrect signs.
- Using the Wrong Base: Always divide by the old value, not the new value.
- Ignoring the Percentage Sign: Always include the percentage sign (%) in the final answer.
- Oversimplification: Avoid oversimplifying complex scenarios by neglecting compounding or weighting.
Conclusion
Calculating percentage change is a versatile tool with numerous applications. Understanding the formula, its variations, and potential pitfalls is crucial for accurate analysis and informed decision-making. By mastering this skill, you'll enhance your ability to interpret data, track trends, and solve problems across various disciplines. Remember to always double-check your calculations and consider the context to ensure accurate interpretations of the results. The 25% increase from 8 to 10 serves as a foundational example, illustrating the power and practicality of understanding percentage change. From simple everyday calculations to complex financial models, this fundamental concept remains essential for navigating a data-driven world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Uv Is Best To Tan
May 12, 2025
-
8 Cuartos De Galon A Litros
May 12, 2025
-
How Many Minutes Until 1 Pm
May 12, 2025
-
What Is 6 9 In Simplest Form
May 12, 2025
-
9 Of 24 Is What Percent
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Is The Percent Of Change From 8 To 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.