How Do You Calculate Watts Per Hour
Treneri
Apr 05, 2025 · 5 min read
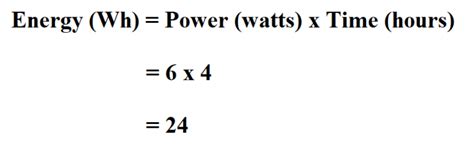
Table of Contents
How Do You Calculate Watts Per Hour? Understanding Power and Energy
The question "how do you calculate watts per hour?" reveals a common misunderstanding about the units of power and energy. Watts (W) measure power, the rate at which energy is used or generated. Watt-hours (Wh) or kilowatt-hours (kWh) measure energy, the total amount of work done over a period. You don't calculate watts per hour; instead, you calculate watt-hours (or kilowatt-hours) to determine energy consumption or production over a specific time. This article will break down the concepts of power and energy, explain how to calculate energy consumption, and explore various applications.
Understanding the Difference Between Watts and Watt-Hours
Let's clarify the fundamental difference:
-
Watts (W): This unit measures power, which is the rate at which energy is consumed or produced. Think of it like the speed of a car – it tells you how quickly energy is being used, not the total distance traveled. A 100-watt light bulb uses energy at a rate of 100 joules per second.
-
Watt-hours (Wh) or Kilowatt-hours (kWh): These units measure energy, which is the total amount of energy consumed or produced over a period. Think of it like the distance a car travels – it tells you the total amount of energy used over time. A 100-watt light bulb running for one hour consumes 100 watt-hours (Wh) of energy.
Calculating Watt-Hours (Wh) and Kilowatt-Hours (kWh)
The basic formula for calculating energy consumption is:
Energy (Wh) = Power (W) × Time (h)
This simple equation allows you to determine the total energy used by a device over a specific time. Let's illustrate with some examples:
Example 1: A 60-watt light bulb burning for 5 hours.
Energy (Wh) = 60 W × 5 h = 300 Wh
This means the light bulb consumed 300 watt-hours of energy.
Example 2: A 1500-watt heater running for 30 minutes.
First, convert minutes to hours: 30 minutes = 0.5 hours
Energy (Wh) = 1500 W × 0.5 h = 750 Wh
The heater consumed 750 watt-hours of energy.
Example 3: A 2 kilowatt (kW) appliance running for 2 hours.
Since 1 kW = 1000 W, we can convert the power to watts: 2 kW = 2000 W
Energy (kWh) = 2 kW × 2 h = 4 kWh
This appliance consumed 4 kilowatt-hours of energy. Kilowatt-hours (kWh) are commonly used for larger appliances and energy bills.
Applications and Real-World Scenarios
The ability to calculate watt-hours is crucial in various situations:
-
Estimating energy costs: Your electricity bill is typically measured in kilowatt-hours. By calculating the energy consumption of your appliances, you can better estimate your monthly electricity costs.
-
Sizing solar panels: If you're planning on installing solar panels, you need to determine your daily energy needs to choose the appropriate panel size and capacity. Calculating the watt-hours for your appliances is essential for this process.
-
Designing efficient power systems: In electronics and electrical engineering, understanding power consumption is crucial for designing efficient and reliable power systems. Calculating watt-hours allows engineers to determine battery size and power supply requirements.
-
Monitoring energy use: Smart home devices and energy monitors provide real-time data on energy consumption. Understanding watt-hours allows you to identify energy-guzzling appliances and make informed decisions about energy-saving measures.
-
Understanding appliance specifications: Many appliances list their power consumption in watts, and you can use this information to calculate their energy use over time.
Factors Affecting Energy Consumption
Several factors influence the actual energy consumption of an appliance beyond the rated wattage:
-
Efficiency: Appliances have varying levels of efficiency. A more efficient appliance will use less energy to perform the same task.
-
Usage patterns: How frequently and for how long you use an appliance significantly impacts its total energy consumption.
-
Operating conditions: Factors like ambient temperature, load, and voltage can affect the actual power draw of an appliance.
Beyond the Basics: Power Factor and Reactive Power
For those familiar with AC electricity, the calculation becomes slightly more complex. The concept of power factor comes into play. Power factor represents the ratio of real power (watts) to apparent power (volt-amperes, VA). Reactive power, measured in volt-amperes reactive (VAR), does not contribute to actual work but still draws current.
In purely resistive loads (like incandescent light bulbs), the power factor is 1. However, in inductive loads (like motors and transformers), the power factor is less than 1, meaning the apparent power is higher than the real power. To calculate the actual energy consumption, you need to consider the power factor:
Real Power (W) = Apparent Power (VA) × Power Factor
Common Mistakes to Avoid
-
Confusing watts and watt-hours: Remember, watts measure power (rate of energy use), while watt-hours measure energy (total amount of energy used over time).
-
Ignoring time: The time duration is a critical component of the energy calculation. Failing to account for it will lead to inaccurate results.
-
Not converting units: Ensure all units are consistent (watts, hours, kilowatt-hours) before performing the calculation.
-
Ignoring power factor (for AC circuits): For AC circuits with inductive or capacitive loads, neglecting the power factor will lead to inaccurate calculations.
Conclusion
Calculating energy consumption in watt-hours (or kilowatt-hours) is a fundamental skill for anyone looking to understand and manage their energy use. By mastering this simple calculation and understanding the difference between power and energy, you can make informed decisions about energy efficiency, cost savings, and sustainable practices. Remember to always consider the factors that can influence energy consumption to get a more accurate estimation of your energy needs. With a bit of practice, you'll become proficient in calculating watt-hours and managing your energy consumption effectively.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Long To Tan In 6 Uv
Apr 05, 2025
-
Standard Form To Point Slope Form
Apr 05, 2025
-
How To Figure Out Cycle Time
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Calories Burned Running 3 Miles
Apr 05, 2025
-
How Many Ccf In A Gallon
Apr 05, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Do You Calculate Watts Per Hour . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
